Stiff Neck Botox
Trigger point blocks are commonly used in pain clinics and other medical facilities to treat stiff neck and shoulders. Local anesthetics are injected into the muscles and fascia, and although they are effective immediately, the duration is often one or two days at most, since the effect of the drug itself is halved in five or six hours. In contrast, botulinum injections are effective gradually from 2 to 3 days, and the effect lasts for 3 to 4 months. After that, the effect gradually returns and may be felt for six months to a year.
At our clinic, the muscles of the neck and shoulder injection sites are identified by ultrasonography, and the Botox solution is injected into those muscles without fail. We inject 6 to 12 units per site. In total, 50 to 100 units are injected.
Ultrasound-guided Botox injection
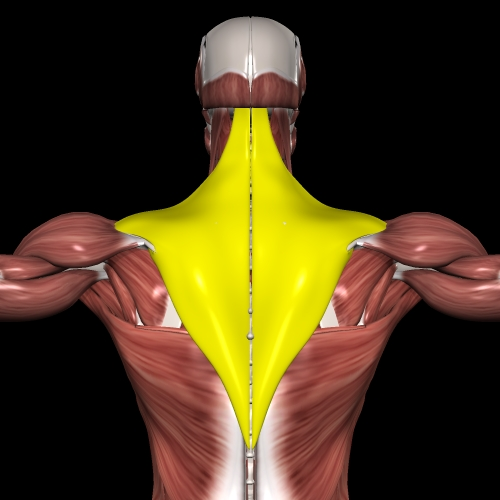
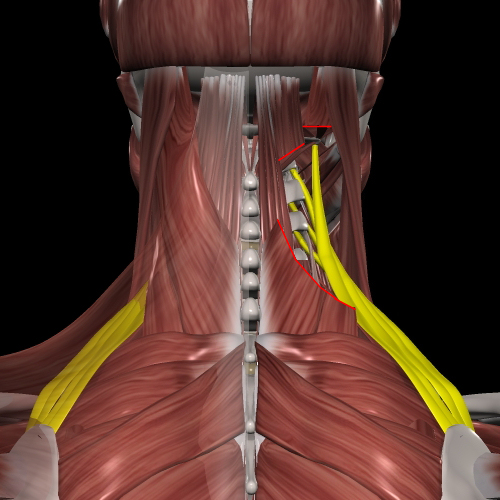
①trapezius muscle
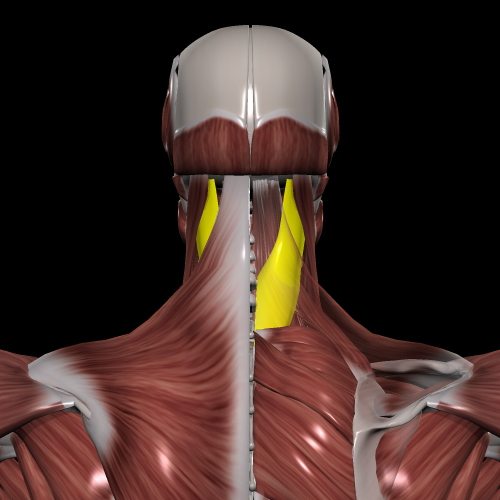
②platysma
③scapulohumeral muscle
Botox for stiff neck and shoulders
Relieves stiffness by partially numbing and relaxing the muscles.
method
First, we use an ultrasound device to diagnose shoulder stiffness. The echo is applied to the area of concern to identify the muscle area under strain, and the needle tip is brought to that muscle belly while viewing the image to inject with pinpoint accuracy.
Side effects
Shoulder heaviness and difficulty in lifting the arm may occur. However, it is not so severe that it interferes with daily life, and it usually disappears within a week or two.
Onset and duration of effect
Effects begin to appear after a few days and almost peak after one or two weeks, and the duration of effect is about four months. Side effects are almost never present, but if they are, they often subside within a few weeks.
Echo-guided injection
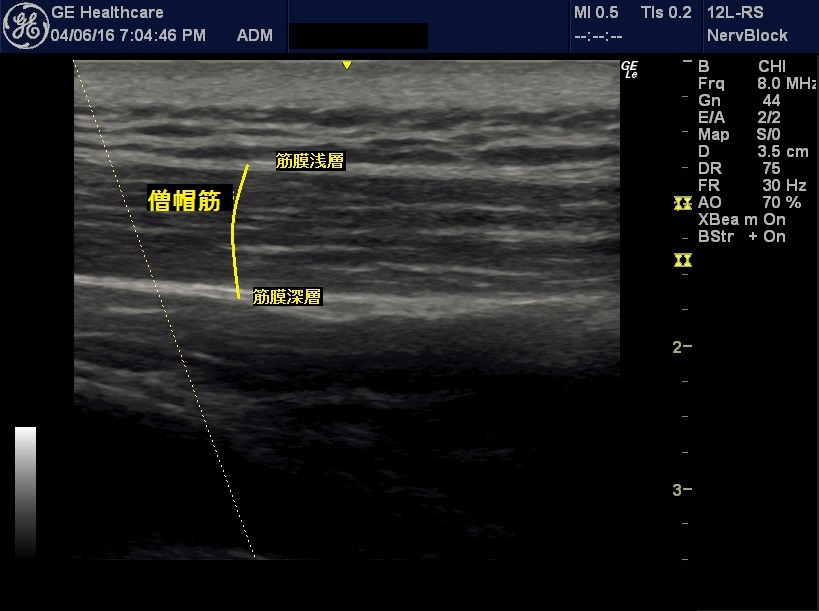
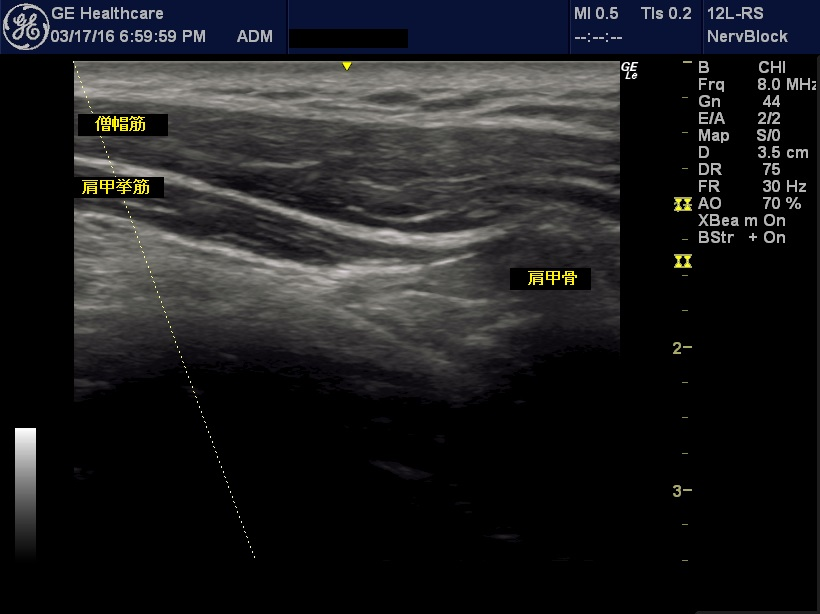
Botox injections are not just to be injected appropriately into the area of a stiff shoulder; they must be injected appropriately into the muscle belly of the muscle that is causing the stiffness. This is because the cause of stiff shoulders is often deeper than the surface muscles. For example, in the case of the shoulder well, the key is not the trapezius muscle, but the levator scapulae muscle, which is deeper than the trapezius muscle. The thickness of the subcutaneous tissue and trapezius muscle varies from person to person. The thickness of the subcutaneous tissue and the trapezius muscle varies from 1 cm to 3 cm, even among people of normal physique. Therefore, in order to inject into the scapularis muscle, which is the muscle that causes shoulder stiffness, it is difficult to inject at the proper point even if the needle is advanced appropriately. In addition, Botox injections are highly diffuse in nature, and must be injected into the muscle belly in order to reduce side effects. Therefore, by advancing the needle tip under echo-guidance and pinpointing the needle tip to the muscle belly of the relevant muscle, Botox injection can be performed safely and reliably.
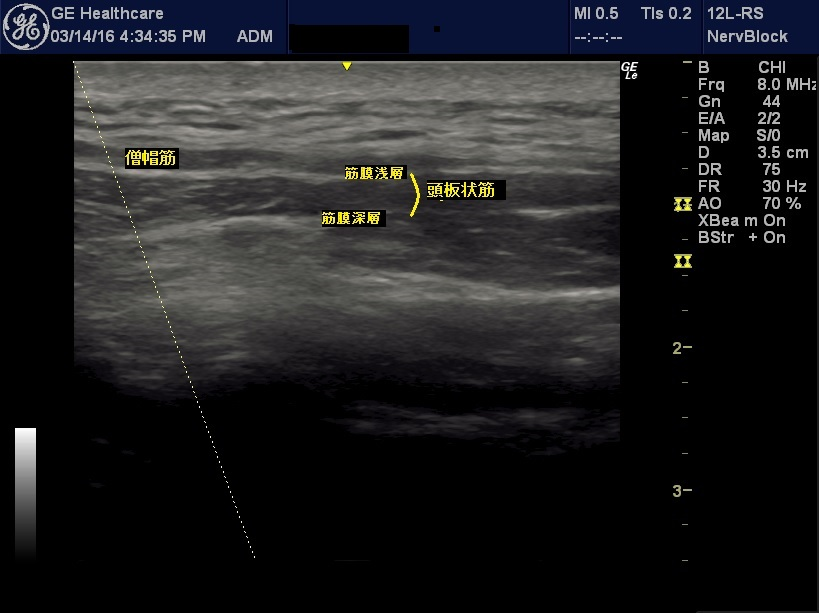
Neck stiffness diagnosis by echo and targeting
Echographic images can be used to diagnose neck and shoulder stiffness. The image immediately reveals the muscles and fascia that are under strain. If you tell us the area of neck and shoulder stiffness that is troubling you, we can place the echo probe on that area and see which muscle and fascia there is strained and causing the neck and shoulder stiffness, and we will inject Botox into the most appropriate muscle belly point to correct the problem. We target the levator scapulae, the platysma, semispinatus, rhomboids, anterior trapezius, pectoralis minor, sternocleidomastoid, and sometimes even the oblique muscles.
Beautiful Neck & Shoulder Botox
Along with neck stiffness, there are also requests for beautiful neck & shoulder (to make the neck look longer and the shoulders flatter). Three places per side may be placed in the trapezius muscle of the muscle bulge. The raised muscle portion of the shoulder can be reduced somewhat. However, I explain that the cause of the shoulder elevation from the front is often the bone (ribs) coming upward, which makes the shoulder look raised and probably does not result in a beautiful shoulder that you will be satisfied with.
In patients with severe shoulder stiffness, for example, the levator scapulae muscle is thick and tense, and Botox injections into the levator scapulae muscle may provide both relief of shoulder stiffness and reduction of muscle bulging. In addition, the sternocleidomastoid muscle may be involved in patients with strong neck tension on both sides, and Botox injections may relieve neck tension and make the neck appear thinner and longer.
Botox for stiff neck
In the case of a stiff neck, in the posterior neck, the relevant muscles are often the platysma and semispinous muscles, which are injected into the middle of the muscle belly with ultrasound images to ensure that they are in the right place. On the side, the oblique and sternocleidomastoid muscles are targeted. The muscle/fascia under strain will show thickening of the fascia and angiogenesis/dilatation on the ultrasound image. In addition to the thickness of the muscle, these factors are evaluated and injected appropriately.
Stiffness inside the shoulder blades
For the medial scapula, injections are made into the large and small rhomboid muscles deep to the trapezius muscle, being careful with ultrasound imaging to ensure that the needle does not penetrate the lungs.
Other Head and Neck Botox
Other injections may be given depending on the location of the head and neck stiffness pain. We often inject Botox into the masseter muscle, temporalis muscle, pectoralis minor muscle, etc.
Problems associated with shoulder stiffness botox
We have injected Botox for stiff shoulders several thousand times without any major side effects and can say that it is an almost safe treatment for stiff shoulders. Some patients may experience some heaviness, but it is not so severe that it interferes with daily life, and it will lessen within a week or two. There are cases where the patient may notice a difference from the injected area, but this may be due to the appearance of a masked area or the strain on other muscles caused by muscle relaxation, and can be treated with additional injections.
About Botulinum Toxin Products
In Japan, botulinum toxin type A (product name: Botox for Injection 50 units and 100 units) was approved as an injectable formulation in 1996 for blepharospasm, 2000 for unilateral facial spasm, 2001 for spastic plagiocephaly, 2009 for spasticity of the lower limbs with spasticity in children with cerebral palsy aged 2 and older, 2010 for upper limb spasticity and In 2010, it was approved for upper limb spasticity and lower limb spasticity, and in 2012, for severe primary axillary hyperhidrosis. Overactive bladder was also recently approved as an indication. In the U.S., the drug is approved for strabismus, spasticity, blepharospasm, spasticity of the upper extremities, and hyperhidrosis, as well as overactive bladder and chronic migraine due to neurological disorders.
In addition, it is often used for "wrinkle removal" and "contouring (gills removal)" by applying its muscle relaxing action in the cosmetic field.
Safety as a pharmaceutical product
In general, botulinum toxin adverse events are transient and are often due to the strong onset of muscle relaxant effects. Most adverse events recover with attenuation of the pharmacologic effects. Usually, minute doses (hundreds to tenths of the estimated lethal dose) are used for medical purposes and are generally safe as long as the dosage regimen is not misadministered.